What is a "Dense" Graph?
In graph theory, density refers to the ratio of actual edges to possible edges.
- Sparse Graph: Has few edges (e.g., a straight line or a tree).
- Dense Graph: Has many edges (e.g., a complete graph where every vertex connects to every other vertex).
The intuition is simple: if you keep adding edges to a graph, eventually, you will be forced to close a loop, creating a cycle. The mathematical challenge is determining exactly when this happens.
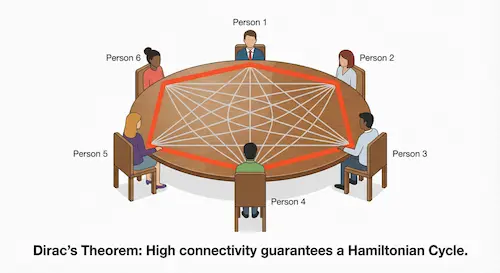
Theorem 1: Dirac’s Theorem (Hamiltonian Cycles)
This is a classic result concerning "Hamiltonian Cycles"—cycles that visit every single vertex exactly once.
The Statement:
If a graph G has n vertices (where n ≥ 3) and every single vertex has a degree of at least n/2, then the graph contains a Hamiltonian cycle.
The Logic:
Imagine a party with n people. If every person knows at least half of the other people there, it is mathematically guaranteed that you can arrange everyone in a circle where each person stands next to two friends.
This theorem is powerful because it relies only on the "minimum degree" condition. It proves that high connectivity (density) locally forces a global structure (the cycle).
Wolfram MathWorld – Dirac’s Theorem – A technical breakdown of the proof logic.
Theorem 2: Turán’s Theorem (The Limit of Edge Density)
Paul Turán took a different approach. He asked: "How many edges can a graph have without containing a specific size of cycle (or clique)?"
The Concept:
Turán’s Theorem gives us an upper bound. It tells us the maximum number of edges a graph can have before it is forced to contain a "complete subgraph" (a clique) of size r.
- Application: If you have a graph with n vertices and you add one more edge than Turán’s limit, you are guaranteed to create a specific cycle structure (like a triangle).
This theorem is fundamental for students needing geometry assignment help because it connects graph theory to geometric structures and extremal combinatorics.
Why Students Struggle with Graph Theory Proofs
Proving these theorems isn't just about calculation; it's about logic.
- Abstract Thinking: You cannot "calculate" the answer; you must construct an argument using induction or contradiction.
- Notation: Confusing G(V, E) with vertex degrees and subgraphs is common.
- Edge Cases: Forgetting constraints (like n ≥ 3) ruins the proof.
If you find yourself thinking, "I need help with my math homework because I can't visualize the proof," you are not alone. Graph theory requires a shift from algebraic thinking to structural thinking.
Why Choose My Perfect Writing for Your Graph Theory Assignments?
Graph theory is rigorous. A single missing step in a proof or an incorrect notation can result in a failed assignment. Here is how My Perfect Writing's specialized service guarantees your academic success.
Free AI Detection Math Reports
ChatGPT struggles with advanced proofs—it often "hallucinates" non-existent theorems. We guarantee 100% human-written solutions. Receive Turnitin®-verified reports ensuring originality, including accurate calculus and graph theory solutions that are aligned with your specific assignment rubric.
Math Solutions by Real Mathematicians
You need an expert, not a chatbot. Get accurate and step-by-step algebra assignment help solved manually by qualified UK math professionals (PhD/Master's holders). We ensure precise notation, logical flow, and academic success in every proof we write.
Guaranteed Grades in Mathematics Assignment
We don't just solve; we perfect. As your trusted math homework helper, we offer geometry assignment help with unlimited revisions. If your professor asks for a clearer step in the proof or a different method, we refine the work until it matches your rubric perfectly.
Pay 25% Upfront for Math Assignment Help
We know math students value accuracy and transparency. Get affordable trigonometry assignment help in the UK with our risk-free model. Pay just 25% upfront to start the work, and the rest only after you have reviewed and approved the solution. No hidden fees.
100% Confidential Math Support
Your academic integrity is paramount. Our secure and discreet assignment handling ensures all your math work remains protected, confidential, and never shared with anyone. Your university will never know you used our support.
24/7 Maths Assignment Help UK
Stuck on a problem set at 2 AM? Get instant support with urgent mathematics assignments, problem-solving tasks, or university-level problems—including linear programming and graph algorithms—anytime you need it. Our team is always online to help you meet the deadline.
Conclusion
The existence of cycles in dense graphs is a mathematical certainty. Whether through Dirac’s focus on minimum degrees or Turán’s focus on edge limits, the math tells us that connections inevitably create loops. Understanding these theorems gives you the power to predict the structure of complex networks, from social media circles to biological ecosystems.
However, moving from the concept to the formal proof can be a stumbling block. If you are staring at your problem set and struggling to construct a logical argument, you don't have to fail.
My Perfect Writing offers the precise, logical, and expert support you need. With our experienced mathematicians and student-friendly payment model, we help you close the loop on your assignment.
Connect the vertices. Prove the theorem.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a cycle and a path?
A path is a sequence of edges connecting distinct vertices (A to B to C). A cycle is a path that starts and ends at the same vertex (A to B to C to A), forming a closed loop.
Why are dense graphs important?
Dense graphs are robust. In computer networking, a dense graph means the network is hard to disconnect. If one link fails, there is likely another cycle that provides an alternative route. This concept is vital for reliability engineering.
Can you help with coding graph algorithms?
Yes. Graph theory is the foundation of computer science. If your assignment involves implementing Dijkstra’s Algorithm or Breadth-First Search (BFS) in Python or Java, our experts can handle the coding and the mathematical theory behind it.
Is Dirac’s Theorem the only way to prove a cycle?
No. Ore’s Theorem is a generalization of Dirac’s. It states that if the sum of degrees of non-adjacent vertices is greater than or equal to n, a Hamiltonian cycle exists. It is less restrictive than Dirac’s.
How do I start a graph theory proof?
Start by defining your terms. "Let G be a graph with n vertices..." Then, state your assumption (e.g., "Assume G has no cycles"). Use logic to reach a contradiction (e.g., "This implies the number of edges is impossible"). This "Proof by Contradiction" is a standard tool we teach students.
Meet Our Professional Essay Writers
Empowering Your Academic Writing Journey with Authority, Expertise, and Experience
Dr. Emma Wilson
PhD in Literature
Prof. James Chen
MSc in Computer Science
Dr. Sarah Ahmed
PhD in Law & Ethics
Ready to Work With Our Expert Writers?